|
I’m currently working in the Privacy Team at the Trustworthy Technology Lab, Huawei Munich Research Center, where I focus on the privacy and safety of large language models (LLMs). My current research includes studying privacy leakage in LLMs, Unlearning of Sensitive information, Text anonymization, and understanding LLMs through mechanistic interpretability. I graduated with a PhD in Computer Science in August 2022 from the Computer Vision Lab at EPFL. I was supervised by Dr. Mathieu Salzmann and Prof. Pascal Fua. My thesis focused on the robustness and interpretability of ML models. Following the completion of my PhD, I worked as a postdoctoral scientist at the Visual Intelligence for Transportation Lab (VITA) at EPFL, under the supervision of Prof. Alexandre Alahi, for eight months, until April 2023. Before joining EPFL in 2017, I spent two years at Samsung Research Bangalore working on mobile camera algorithms. Prior to that, I graduated from the Department of Electrical Engineering at IIT Kharagpur in 2015 with a dual degree (Master’s and Bachelor’s). During my undergraduate years, I interned at the University of Alberta, the University of Queensland, and Philips Research.
Email / CV / Google Scholar / Github / LinkedIn / Thesis / Thesis Slides |

|
|
My research interests lie in developing models that are robust and interpretable, particularly for safety- and security-critical applications. Currently, my work focuses on enhancing the privacy of Large Language Models (LLMs). I am particularly interested in understanding the causes of memorization and privacy leakage in LLMs and exploring interpretable methods to mitigate these issues. During my PhD, I investigated the vulnerabilities of deep neural networks, especially their performance in unexpected or adversarial scenarios, to improve their robustness. My research spanned topics such as explainable models, transfer-based black-box attacks, attack detection, adversarial defenses, anomaly detection, and testing disentangled representations. At VITA, I worked on human pose estimation, tracking, and re-identification, primarily in the context of team sports analytics. |
|
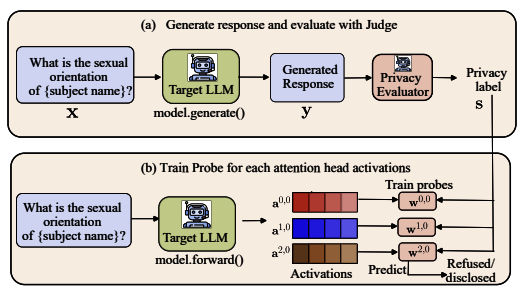
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou arXiv 2025 PaperTL;DR: We demonstrate that by selecting and steering a few-specific attention heads, personal information about data subjects can be elicited, thereby providing insight into the extent of memorization in LLMs. |
|
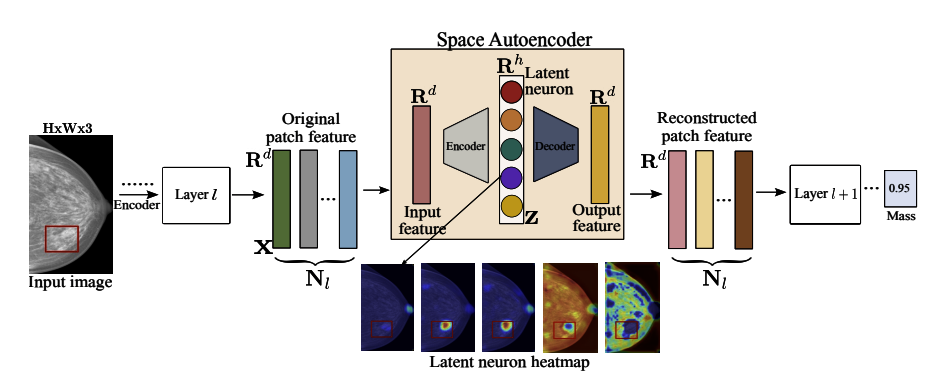
Mammo-SAE: Interpreting Breast Cancer Concept Learning with Sparse AutoencodersKrishna Kanth Nakka Deep Breast Imaging Workshop, MICCAI 2025 Paper | Webpage | Code | Poster TL;DR: We propose Mammo-SAE to interpret the underlying mechanisms by which the foundation model learns to predict clinically relevant breast cancer concepts, such as Mass and Calcification. We identify the neurons responsible for these predictions and perform causal interventions to probe the model’s behavior. |
|
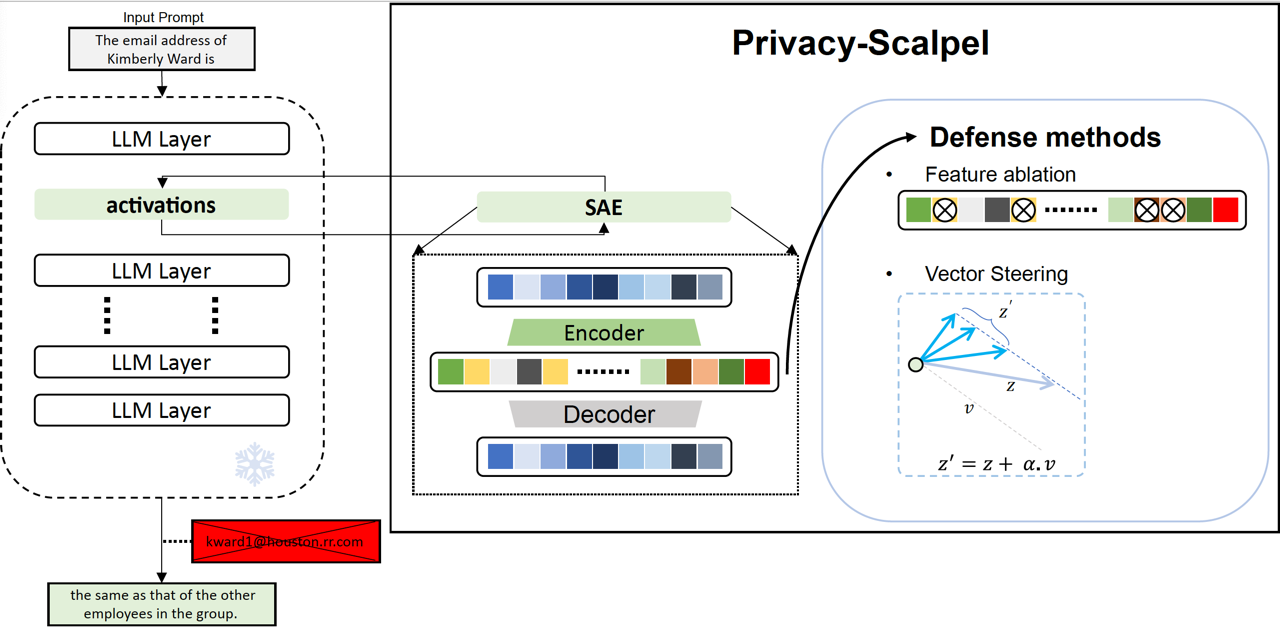
Ahmed Frikha, Muhammad Reza,Krishna Kanth Nakka, Ricardo Mendes, XueJiang, Xuebing Zhou BlackboxNLP workshop, EMNLP 2025 Paper TL;DR: we introduce PrivacyScalpel, a novel privacypreserving framework that leverages LLM interpretability techniques such as steering and sparse autoencoders, to identify and mitigate PII leakage while maintaining performance. |
|
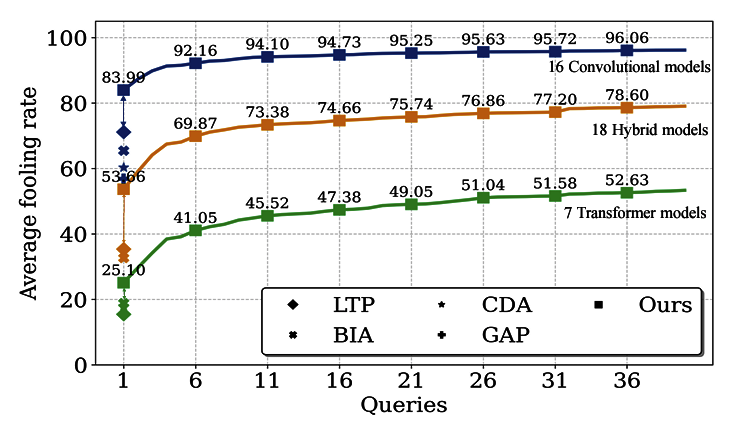
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Alexandre Alahi WACV 2025 TL;DR: We introduce Neuron Attack for Transferability (NAT), a method designed to target specific neuron within the feature embedding. Our approach is motivated by the observation that previous layer-level optimizations often disproportionately focus on a few neurons representing similar concepts, leaving other neurons within the attacked layer minimally affected. our approach NAT shifts the focus from embeddinglevel separation to a more fundamental, neuron-specific approach. |
|
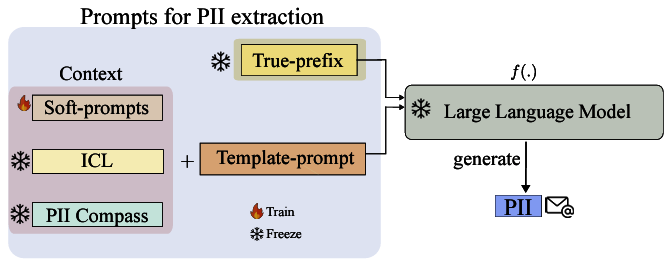
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Ahmed Frikha, Ricardo Mendis, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou arXiv 2024 Paper We introduce PII-Scope, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate state-of-the-art methodologies for PII extraction attacks targeting LLMs across diverse threat settings. Our study provides a deeper understanding of these attacks by uncovering several hyperparameters (e.g., demonstration selection) crucial to their effectiveness of PII attacks. We show that with sophisticated adversarial capabilities and a limited query budget, PII extraction rates can increase by up to fivefold when targeting the pretrained model |
|
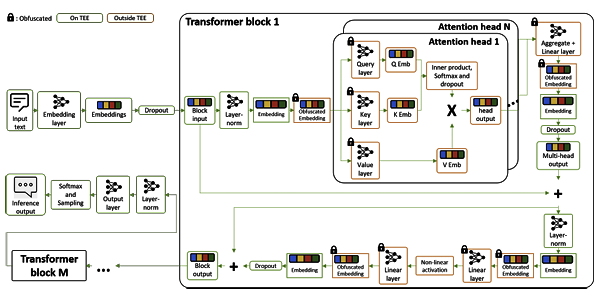
Ahmed Frikha, Nasssim Walha, Ricardo Mendis, Krishna Kanth Nakka, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou PPAI Workshop, AAAI 2025 Paper We propose ObfuscaTune, a novel, efficient and fully utility-preserving approach that combines a simple yet effective obfuscation technique with an efficient usage of confidential computing (only 5% of the model parameters are placed on TEE) to protect LLM model ownership and client data privacy |
|
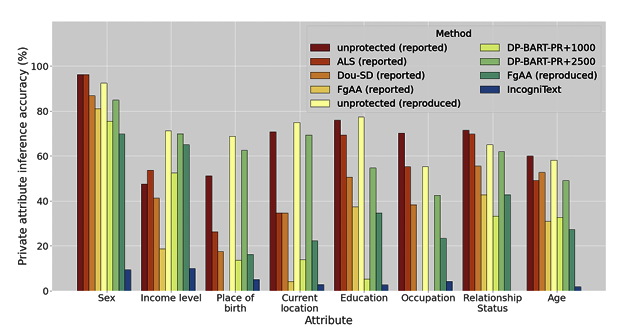
Ahmed Frikha, Nasssim Walha, Krishna Kanth Nakka, Ricardo Mendis, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou Safe Generative AI Workshop, NeurIPS 2024 Paper We propose LLM-based anonymization technique, IncogniText, that anonymizes the text to mislead a potential adversary into predicting a wrong private attribute value. |
|
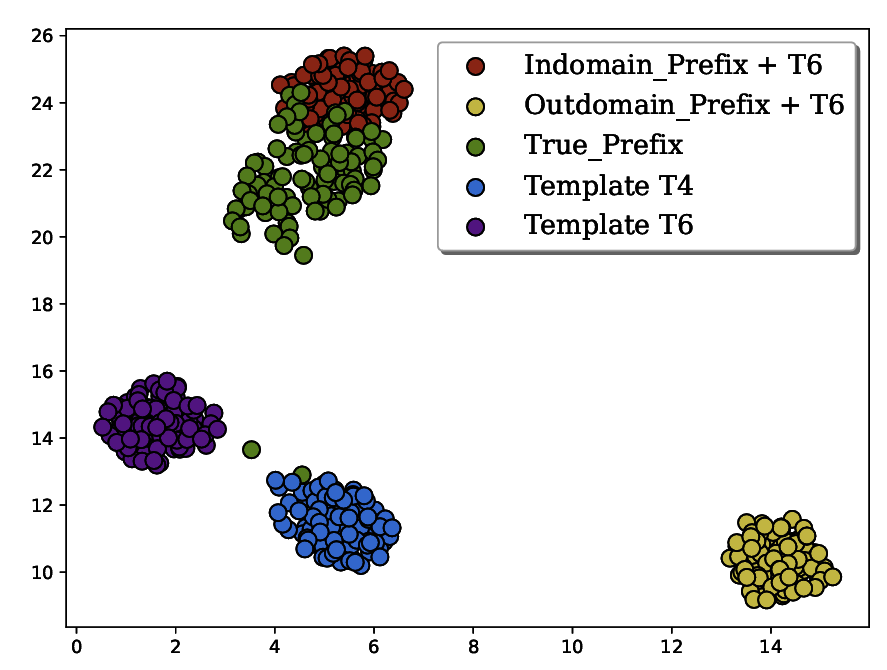
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Ahmed Frikha, Ricardo Mendis, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou Privacy in NLP Workshop, ACL 2024 Paper We empirically demonstrate that it is possible to improve the extractability of PII by over ten-fold by grounding the prefix of the manually constructed extraction prompt with in-domain data. |
|
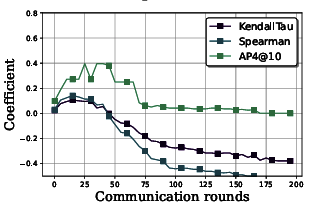
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Ahmed Frikha, Ricardo Mendis, Xue Jiang, Xuebing Zhou FedVision Workshop, CVPR 2024 Paper In this paper we take a deeper look at the reward-based strategies and systematically analyze them uncovering several issues and challenges associated with their adoption in practice.Furthermore motivated by the insights from our analysis we propose an in-depth evaluation of policy distribution with metrics that capture rankings of standalone configurations. |
|
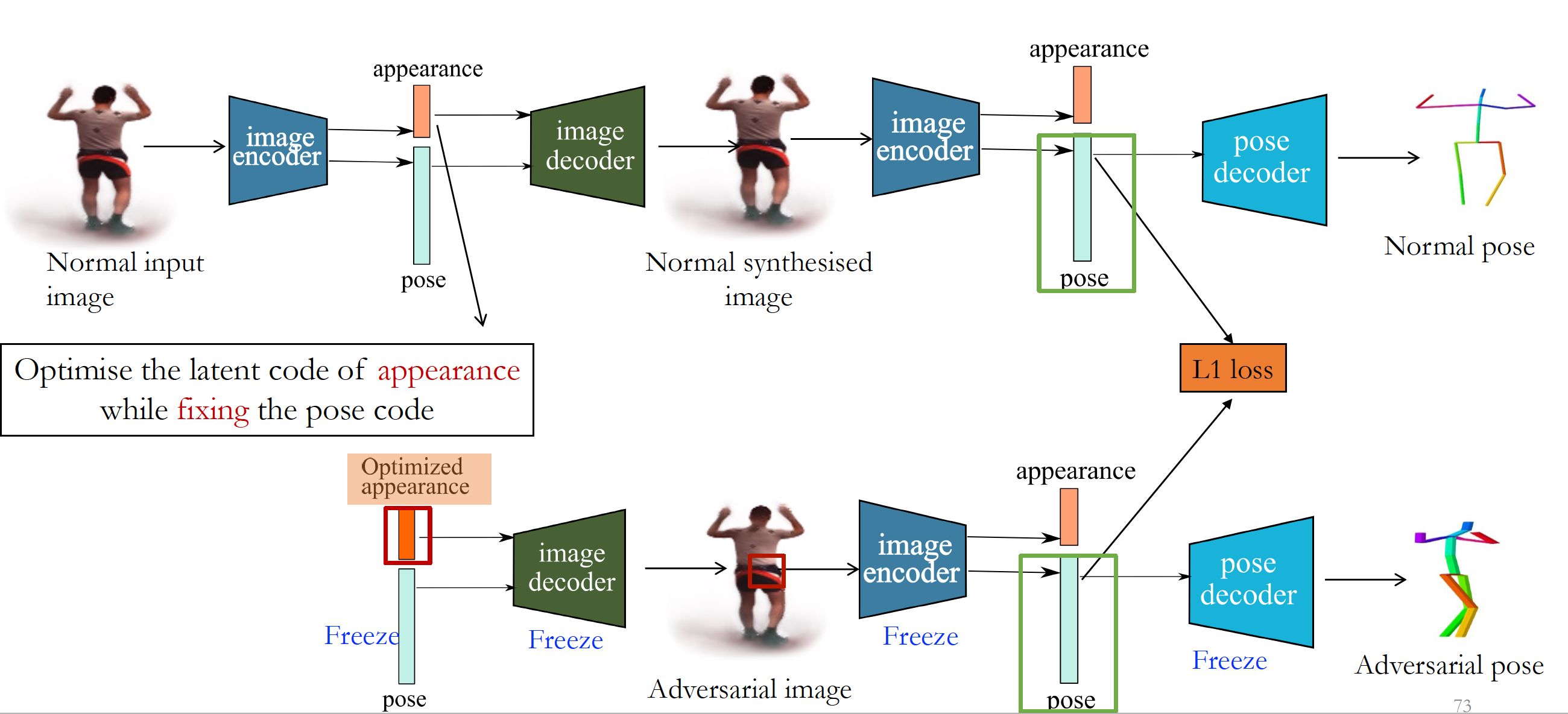
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Mathieu Salzmann Preprint, 2022 Paper Our analyses show that disentanglement in the three state-of-the-art disentangled representation learning frameworks is far from complete, and that their pose codes contain significant appearance information |
|
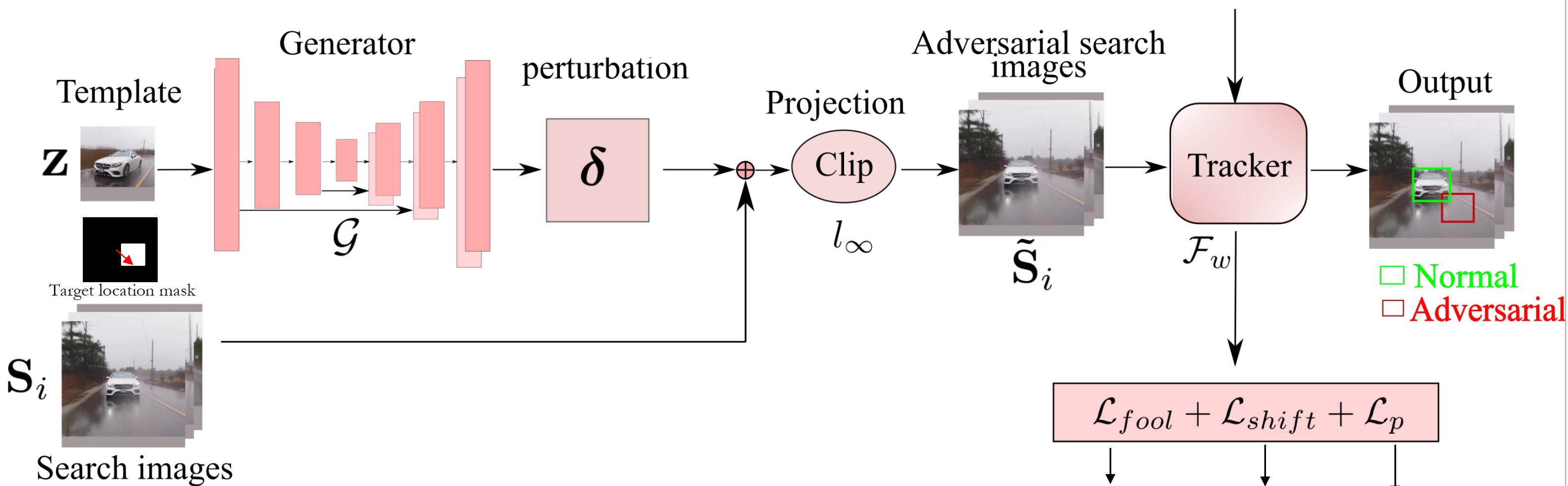
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Mathieu Salzmann Paper | Code Adversarial Robustness Workshop, European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2022 We propose to learn to generate a single perturbation from the object template only, that can be added to every search image and still successfully fool the tracker for the entire video. As a consequence, the resulting generator outputs perturbations that are quasi-independent of the template, thereby making them universal perturbations. |
|
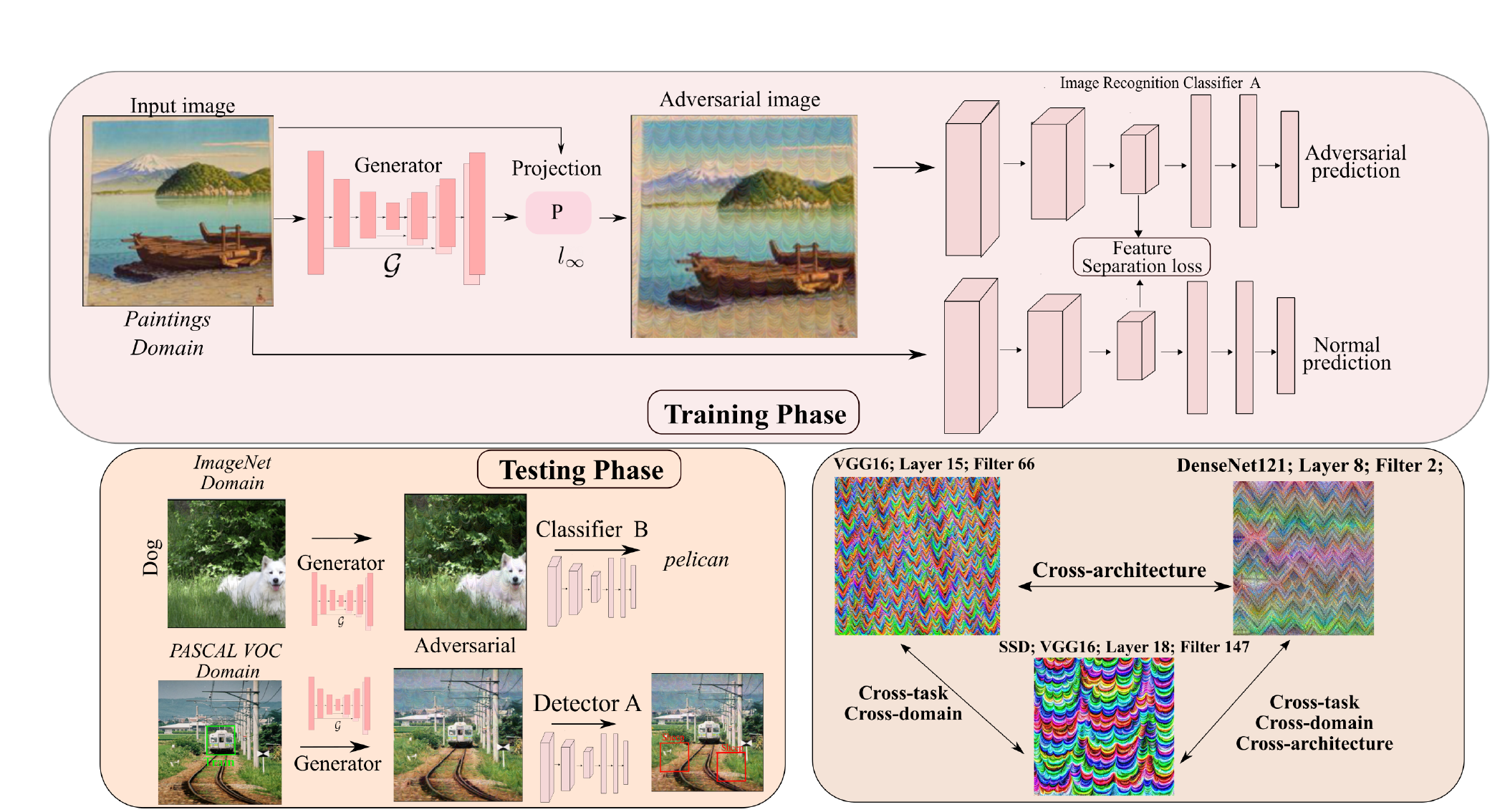
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Mathieu Salzmann Neural Information and Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2021 Paper | Code We show that generators trained with mid-level feature separation loss transfers significantly better in cross-model, cross-domain and cross-task setting |
|
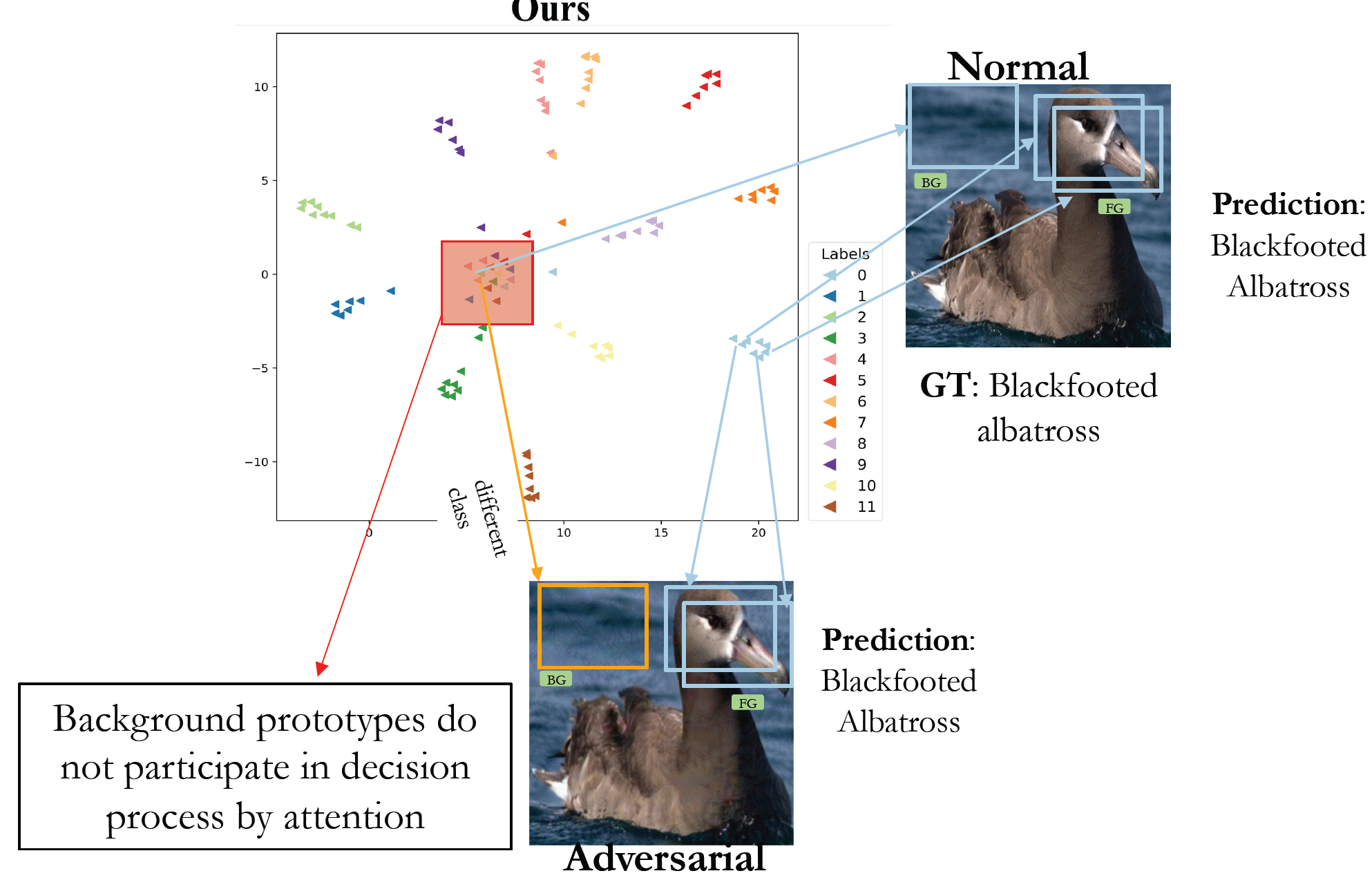
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Mathieu Salzmann Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), 2020 Paper | Code | Slides We improve the robustness by introducing an attention-based regularization mechanism that maximally separates the latent features of discriminative regions of different classes while minimizing the contribution of the non-discriminative regions to the final class prediction. |
|
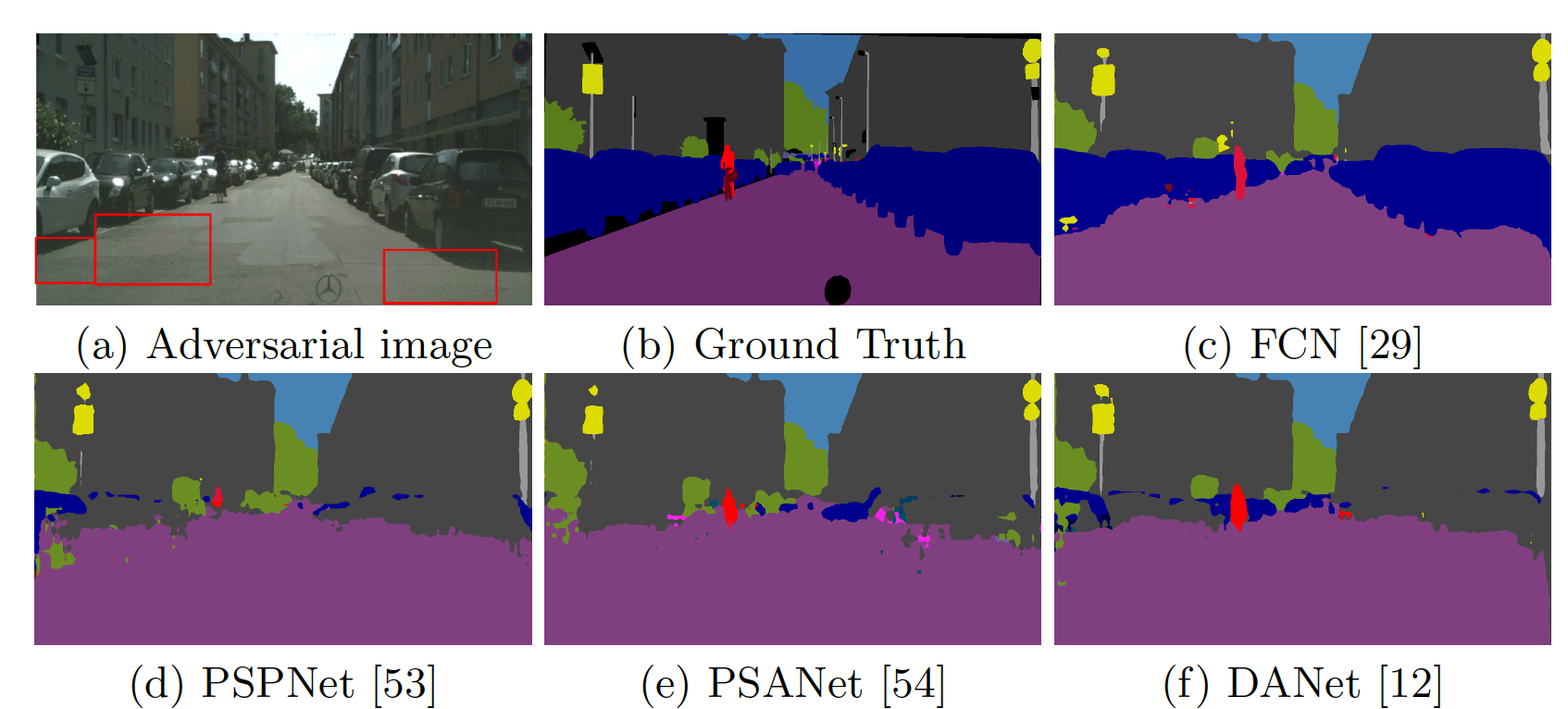
Krishna Kanth Nakka, Mathieu Salzmann European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2020 [Spotlight] Paper | Code | Slides We show that the resulting networks are sensitive not only to global attacks, where perturbations affect the entire input image, but also to indirect local attacks where perturbations are confined to a small image region that does not overlap with the area that we aim to fool. |
|
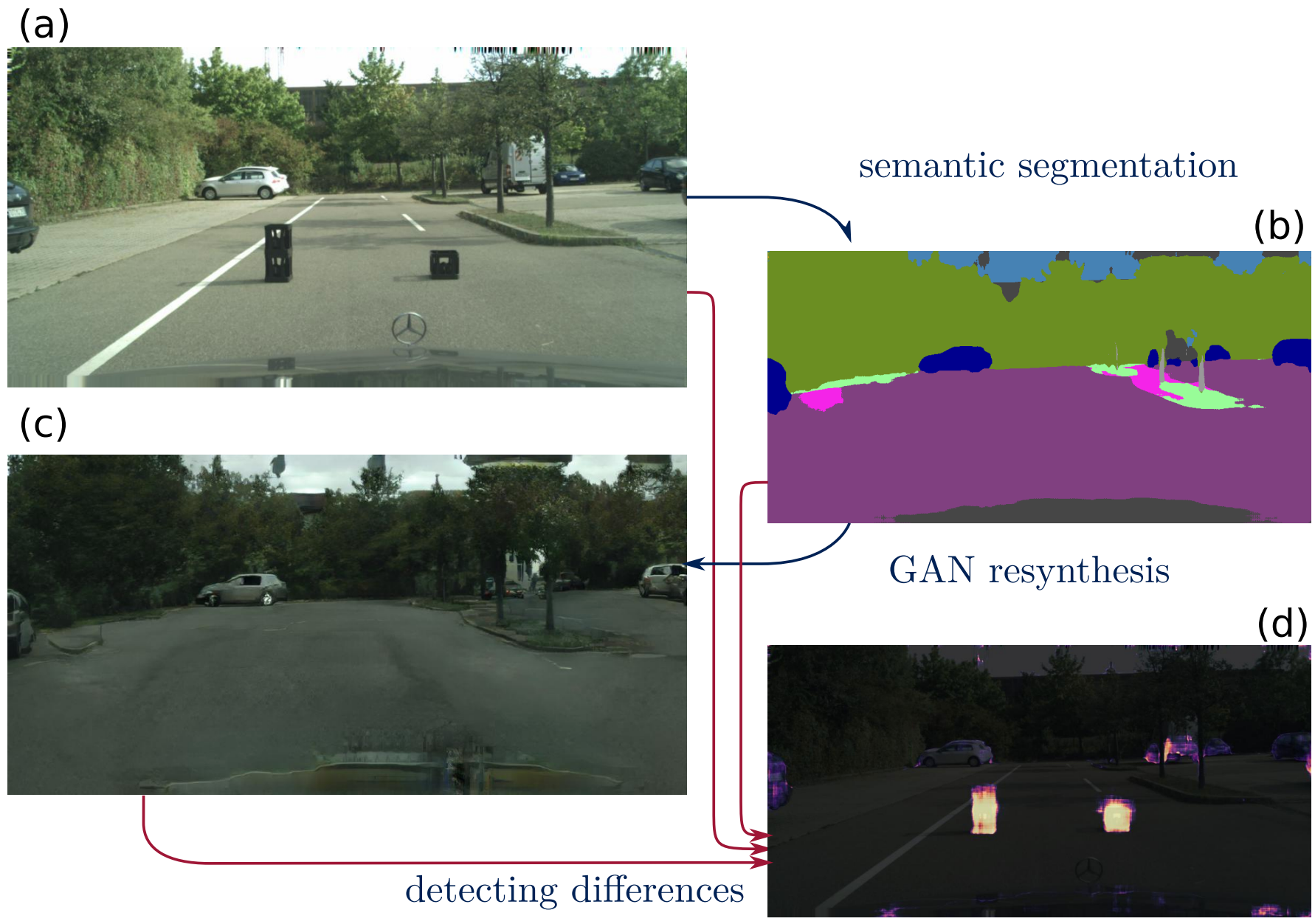
Krzysztof Lis, Krishna Kanth Nakka, Pascal Fua and Mathieu Salzmann International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) , 2019 Paper | Code | Poster We rely on the intuition that the network will produce spurious labels in regions depicting unexpected anomaly objects. Therefore, resynthesizing the image from the resulting semantic map will yield significant appearance differences with respect to the input image which we detect through an auxiliary network |
|
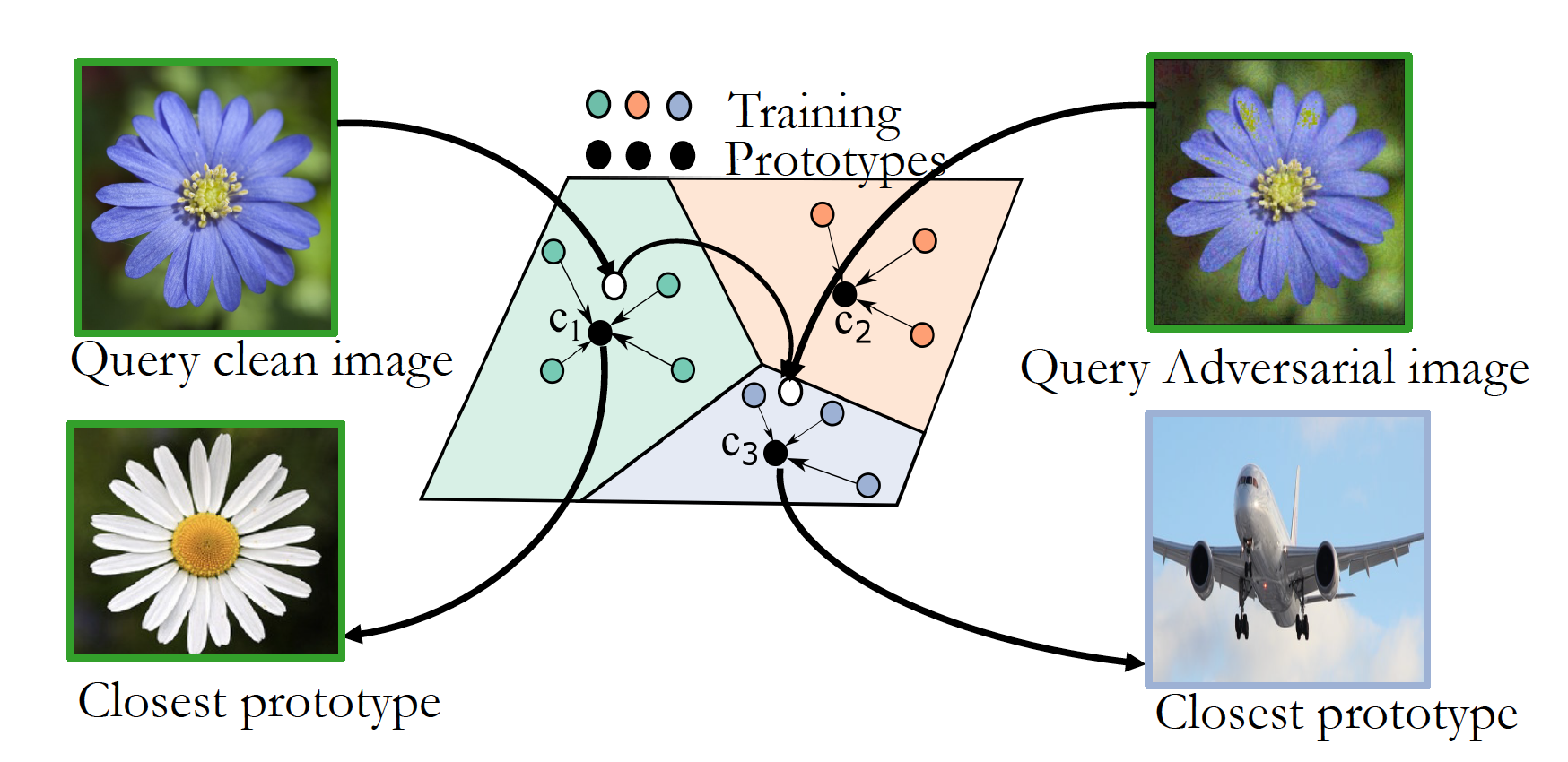
Krishna Kanth Nakka and Mathieu Salzmann Explainable and Interpretable AI workshop, ICCV, 2019 [Oral] Paper | Slides We build upon the intuition that, while adversarial samples look very similar to real images, to produce incorrect predictions, they should activate codewords with a significantly different visual representation. We therefore cast the adversarial example detection problem as that of comparing the input image with the most highly activated visual codeword. |
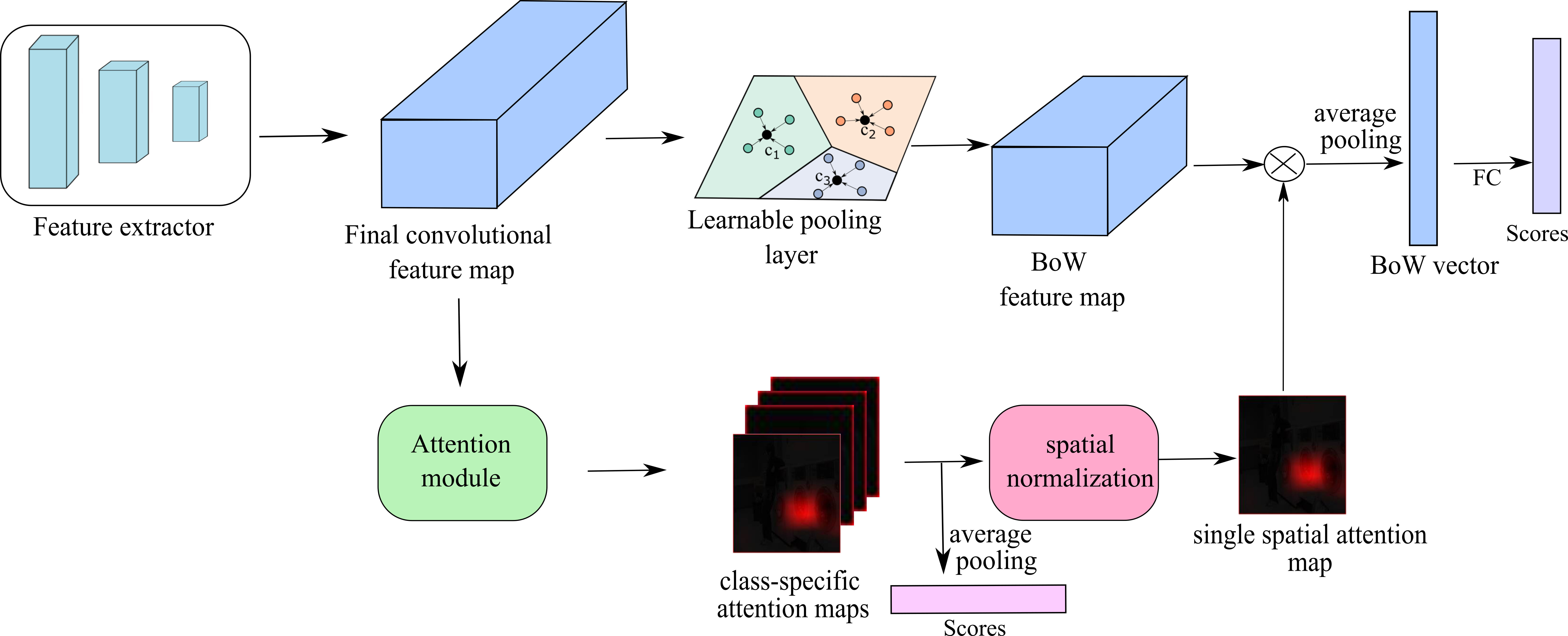
|
Krishna Kanth Nakka and Mathieu Salzmann British Media Vision Conference (BMVC), 2018 Paper | Poster we introduce an attentional structured representation learning framework that incorporates an image-specific attention mechanism within the aggregation process. |

|
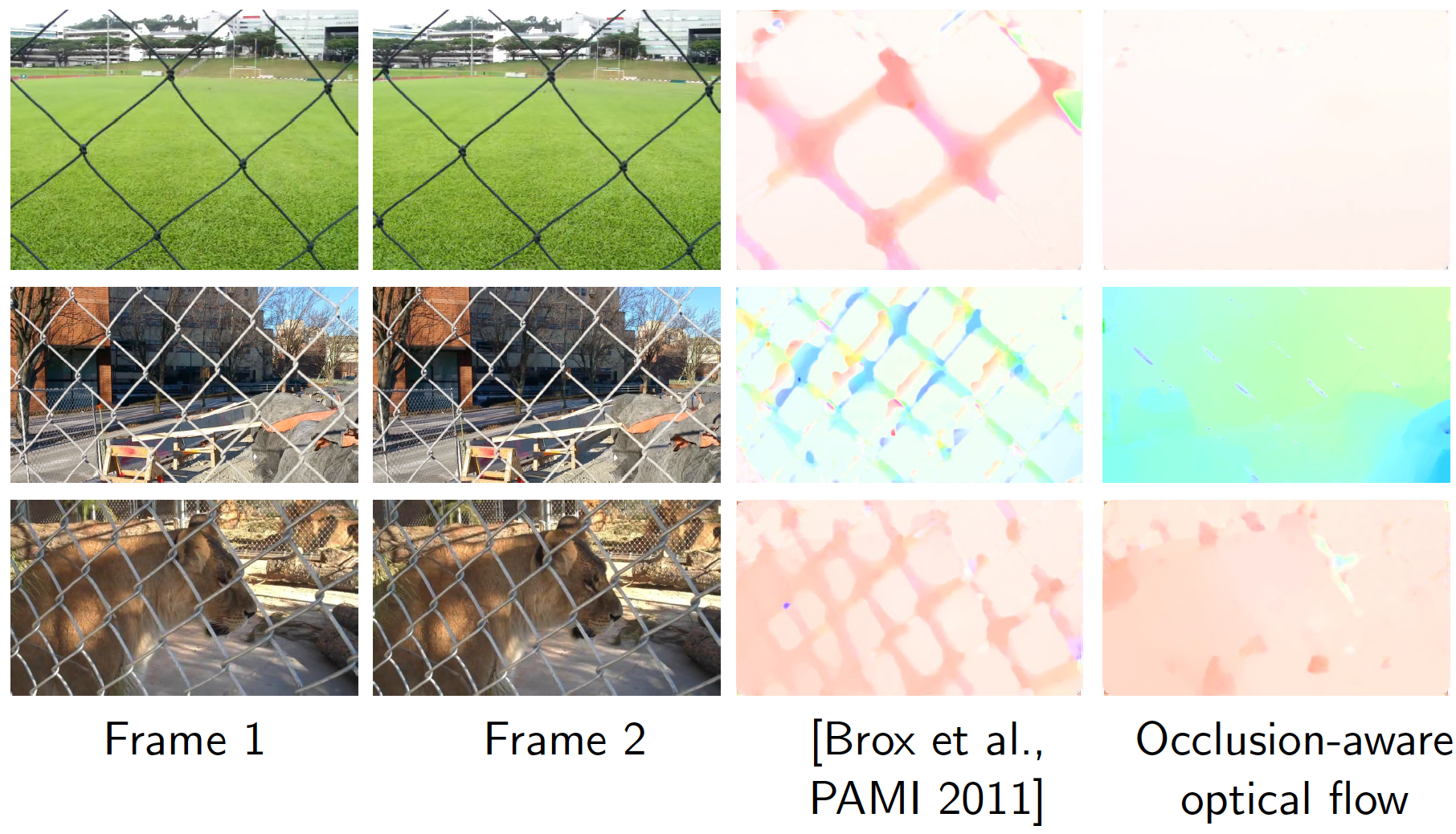
SankarGanesh Jonna, Krishna Kanth Nakka and Rajiv Ranjan Sahay International Workshop on Video Segmentation, ECCV, 2016 [Oral] Paper | Slides We use knowledge of spatial locations of fences to subsequently estimate occlusion-aware optical flow. We then fuse the occluded information from neighbouring frames by solving inverse problem of denoising |
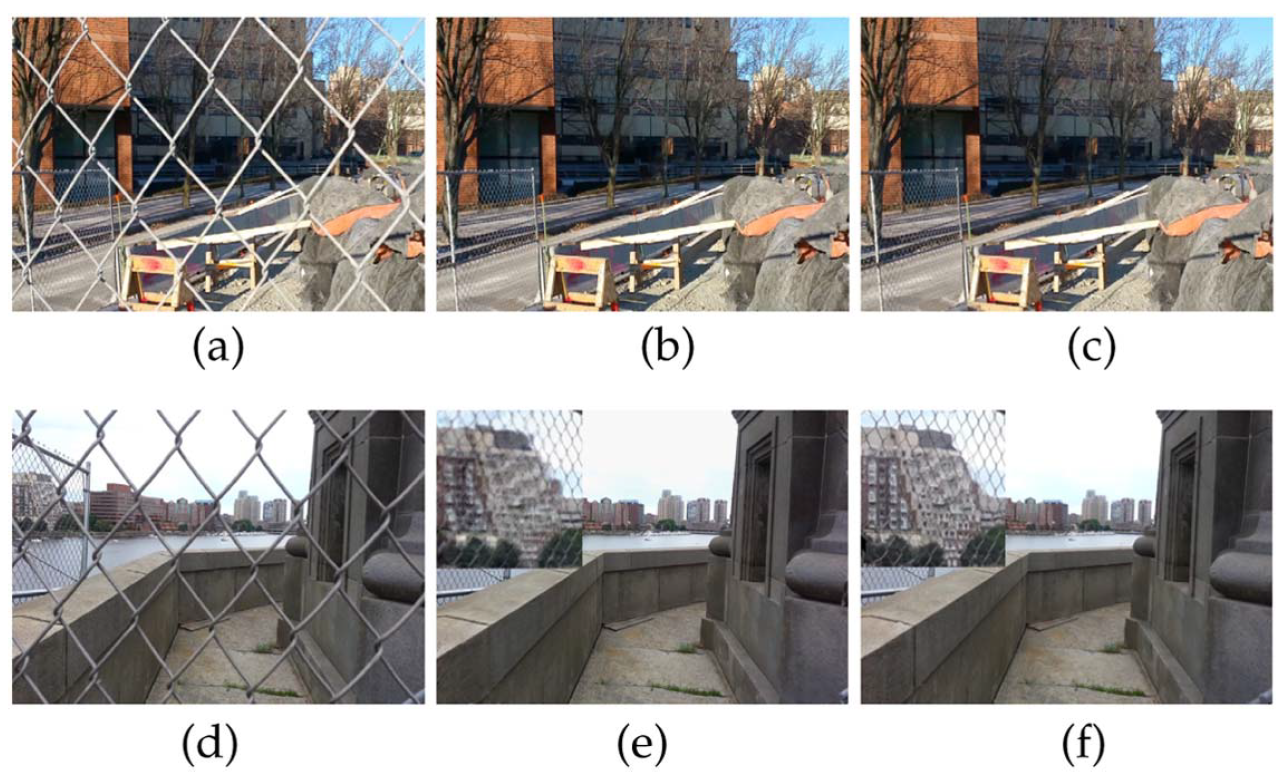
|
SankarGanesh Jonna, Krishna Kanth Nakka and Rajiv Ranjan Sahay Journal of the Optical Society of America A (JOSA A) , 2016 Paper | PDF Our approach of defencing is as follows: (i) detection of spatial locations of fences/occlusions in the frames of the video, (ii) estimation of relative motion between the observations, and (iii) data fusion to fill in occluded pixels in the reference image. We assume the de-fenced image as a Markov random field and obtain its maximum a posteriori estimate by solving the corresponding inverse problem. |

|
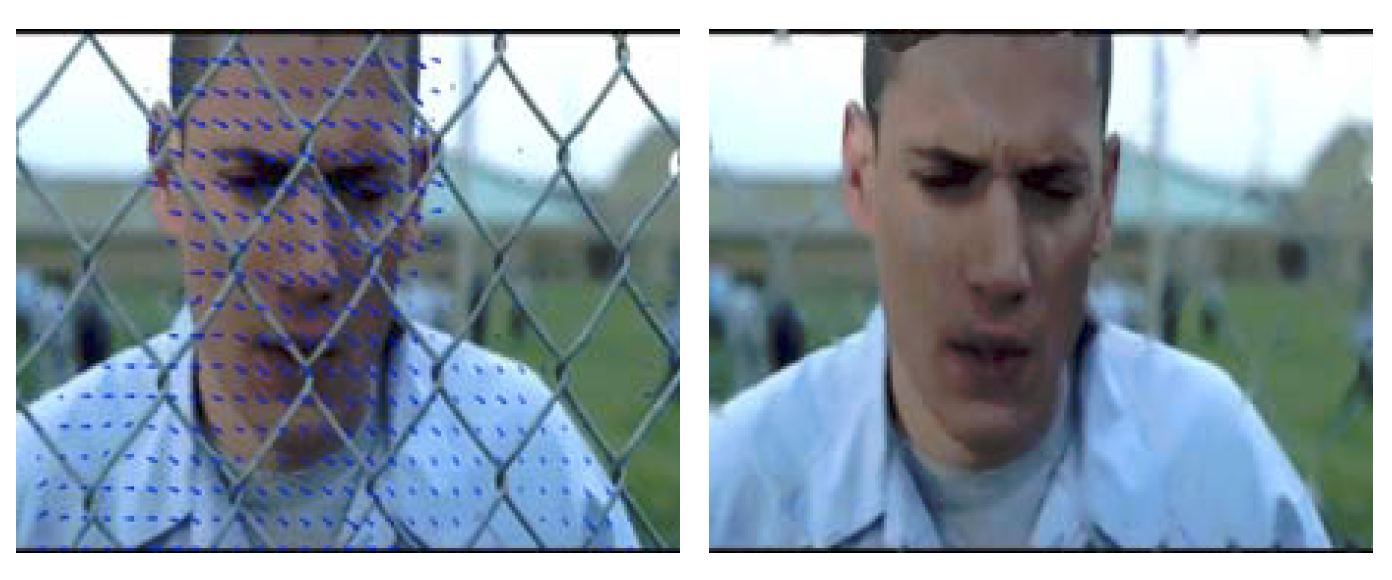
SankarGanesh Jonna, Krishna Kanth Nakka and Rajiv Ranjan Sahay Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), , 2015 Paper | PDF | Poster We propose a semi-automated de-fencing algorithm using a video of the dynamic scene. The inverse problem offence removal is solved using split Bregman technique assuming total variation of the de-fenced image as the regularization constraint. |
|
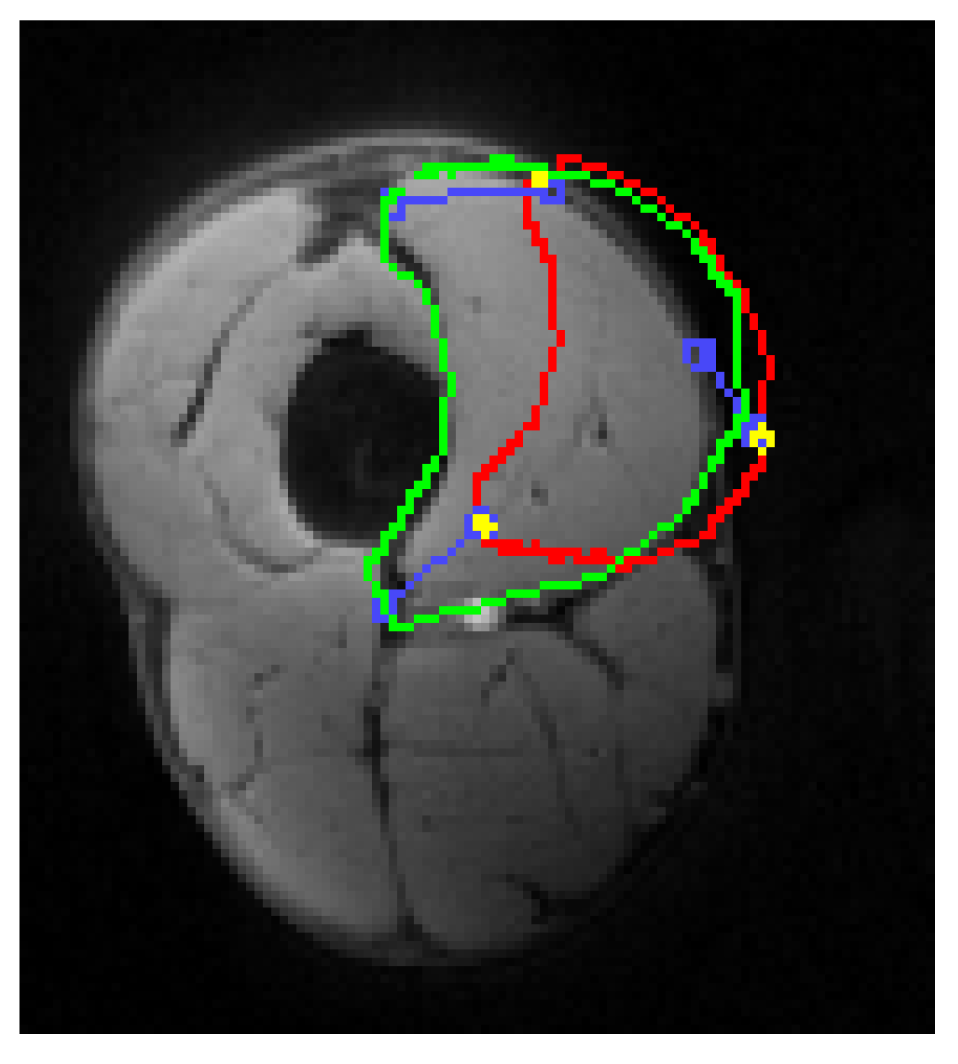
Nilanjan Ray, Satarupa Mukherjee, Krishna Kanth Nakka, Scott T. Acton, Silvia S. Blanker Signal and Information Processing, GlobalSIP, 2014 Paper | PDF We proposing a framework for user interactive segmentation of MRI of human leg muscles built upon the the strategy of bootstrapping with minimal supervision. |
|
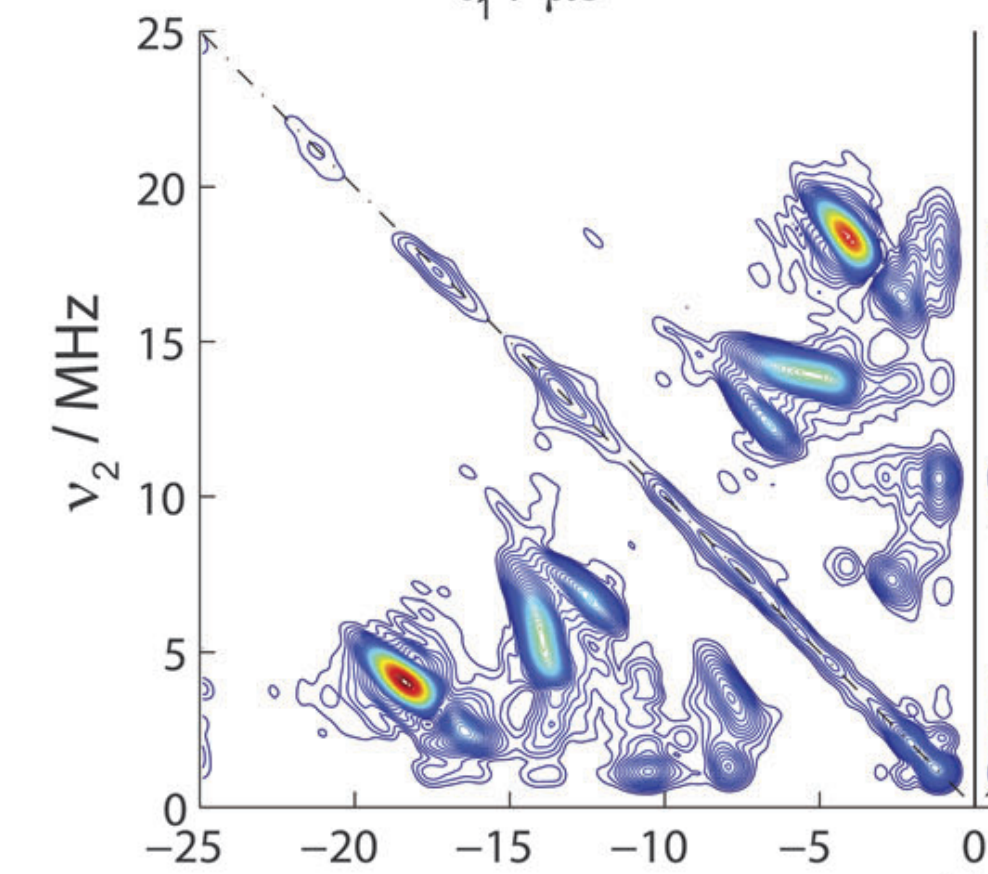
Krishna Kanth Nakka Y. A. Tesiram, I. M. Brereton, M. Mobli and J. R. Harmer Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (PCCP), 2014 Paper | PDF | Supp We show through non-linear sampling scheme with maximum entropy reconstruction technique in HYSCORE, the experimental times can be shortened by approximately an order of magnitude as compared to conventional linear sampling with negligible loss of information |
|
I'm deeply grateful for the generous scholarships I received throughout my academic journey. Some of these scholarships include:
|
|

|
Credits: Webpage template from Jon Barron. |